Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2025
-
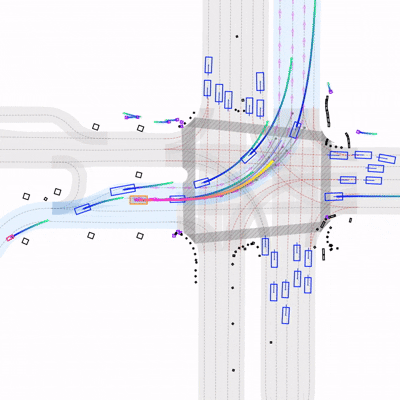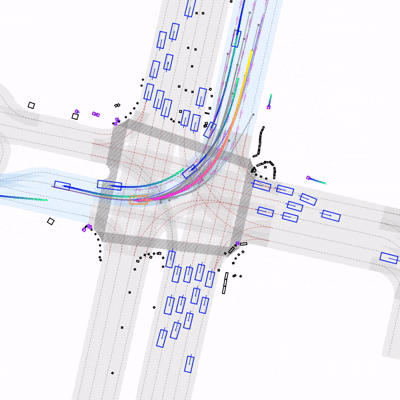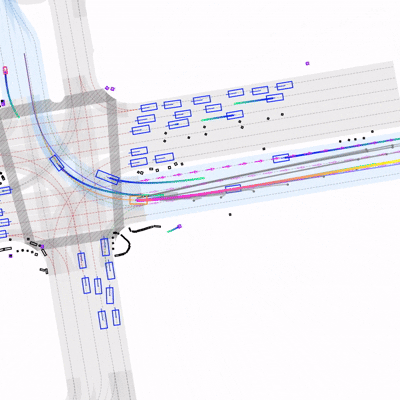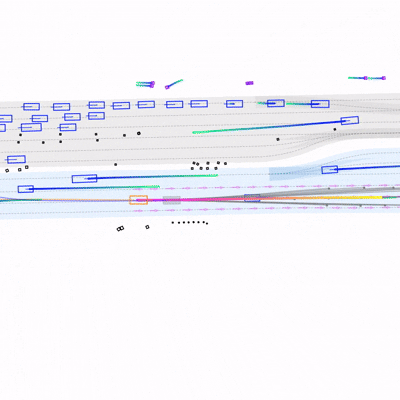 Learning to Drive by Imitating Surrounding VehiclesYasin Sonmez, Hanna Krasowski, and Murat Arcak2025
Learning to Drive by Imitating Surrounding VehiclesYasin Sonmez, Hanna Krasowski, and Murat Arcak2025Imitation learning is a promising approach for training autonomous vehicles (AV) to navigate complex traffic environments by mimicking expert driver behaviors. However, a major challenge in this paradigm lies in effectively utilizing available driving data, as collecting new data is resource-intensive and often limited in its ability to cover diverse driving scenarios. While existing imitation learning frameworks focus on leveraging expert demonstrations, they often overlook the potential of additional complex driving data from surrounding traffic participants. In this paper, we propose a data augmentation strategy that enhances imitation learning by leveraging the observed trajectories of nearby vehicles, captured through the AV’s sensors, as additional expert demonstrations. We introduce a vehicle selection sampling strategy that prioritizes informative and diverse driving behaviors, contributing to a richer and more diverse dataset for training. We evaluate our approach using the state-of-the-art learning-based planning method PLUTO on the nuPlan dataset and demonstrate that our augmentation method leads to improved performance in complex driving scenarios. Specifically, our method reduces collision rates and improves safety metrics compared to the baseline. Notably, even when using only 10% of the original dataset, our method achieves performance comparable to that of the full dataset, with improved collision rates. Our findings highlight the importance of leveraging diverse real-world trajectory data in imitation learning and provide insights into data augmentation strategies for autonomous driving.
2024
-
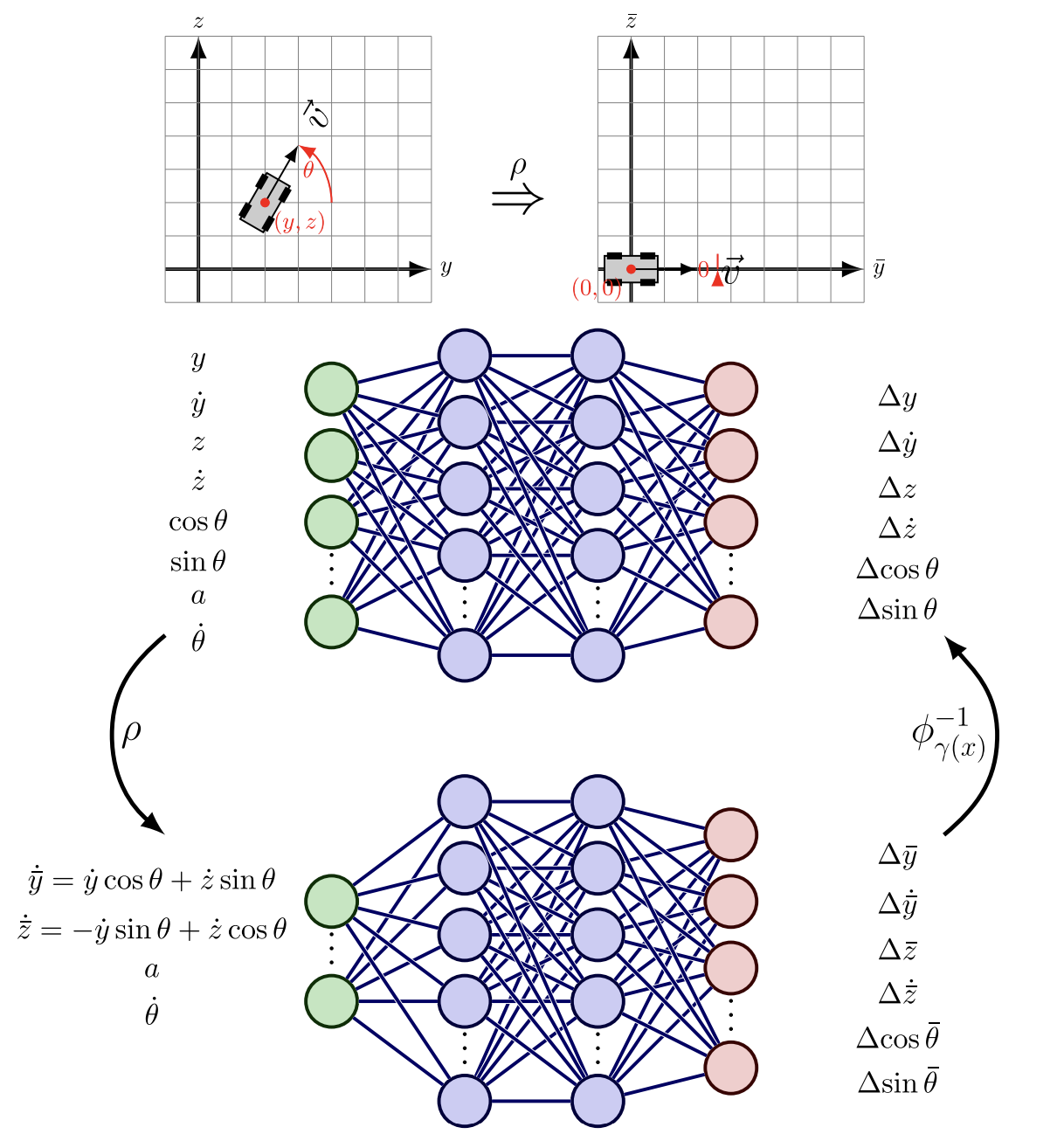 Exploiting Symmetry in Dynamics for Model-Based Reinforcement Learning With Asymmetric RewardsYasin Sonmez, Neelay Junnarkar, and Murat ArcakIEEE Control Systems Letters, 2024
Exploiting Symmetry in Dynamics for Model-Based Reinforcement Learning With Asymmetric RewardsYasin Sonmez, Neelay Junnarkar, and Murat ArcakIEEE Control Systems Letters, 2024Recent work in reinforcement learning has leveraged symmetries in the model to improve sample efficiency in training a policy. A commonly used simplifying assumption is that the dynamics and reward both exhibit the same symmetry; however, in many real-world environments, the dynamical model exhibits symmetry independent of the reward model. In this letter, we assume only the dynamics exhibit symmetry, extending the scope of problems in reinforcement learning and learning in control theory to which symmetry techniques can be applied. We use Cartan’s moving frame method to introduce a technique for learning dynamics that, by construction, exhibit specified symmetries. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed method learns a more accurate dynamical model.
-
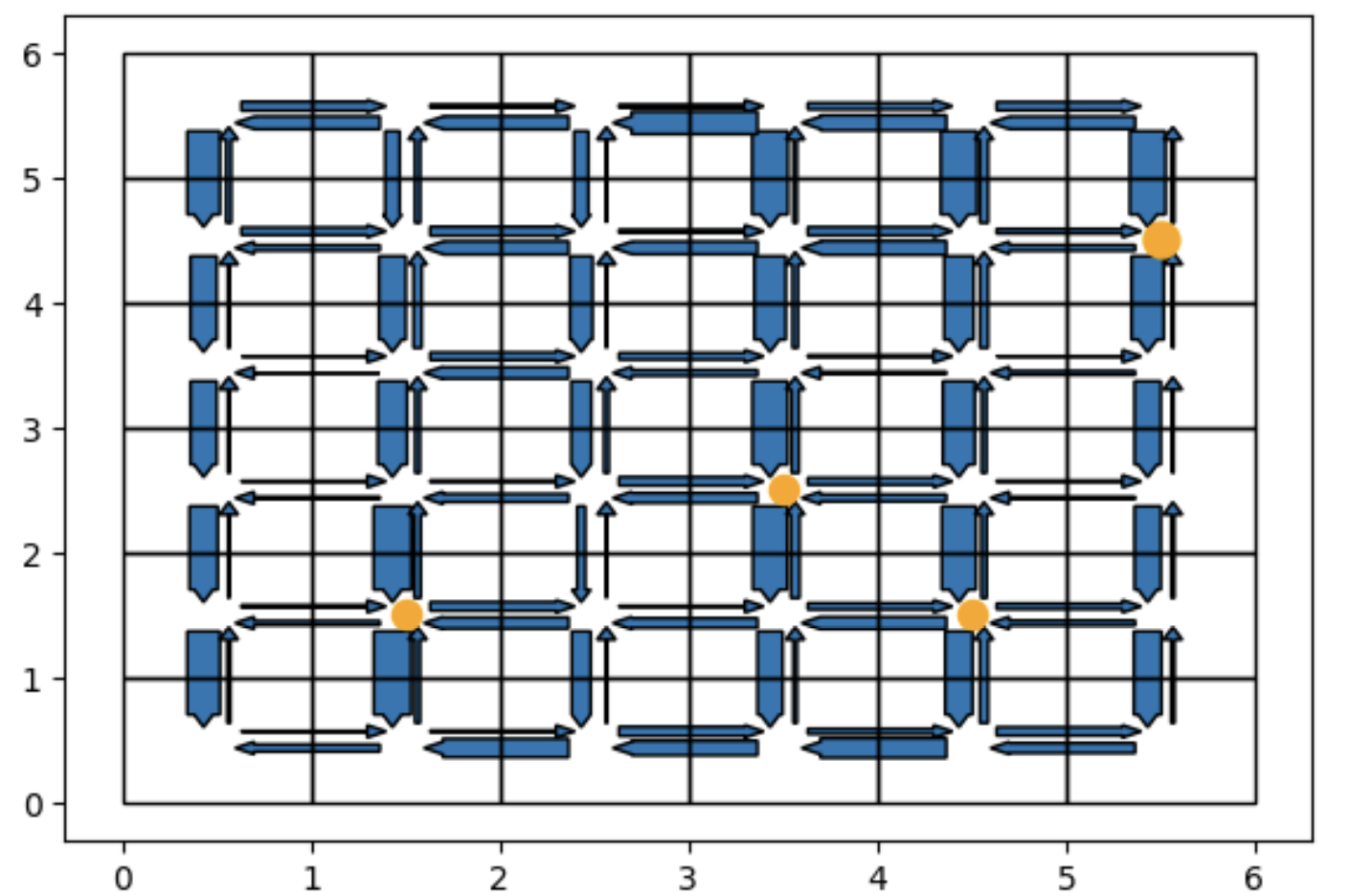 Optimal Electric Vehicle Charging Station Placement as a Congestion Game ProblemYasin Sonmez, Can Kizilkale, Alex Kurzhanskiy, and 1 more authorIn 2024 European Control Conference (ECC), 2024
Optimal Electric Vehicle Charging Station Placement as a Congestion Game ProblemYasin Sonmez, Can Kizilkale, Alex Kurzhanskiy, and 1 more authorIn 2024 European Control Conference (ECC), 2024We propose an optimization method to place electric vehicle charging stations to minimize total travel time, thereby minimizing additional congestion and detours caused by the chargers. For a tractable optimization scheme, we frame the drivers’ route choices as a congestion game that allows us to find equilibrium flows for each candidate set of locations. Our contribution has two primary components. First, we refine the modeling of driver cost functions to account for charging needs as well as travel time, and introduce different agent types based on their unique valuations of charging benefits. Second, we address the exponential growth of the search space of charger locations with a greedy optimization approach. We demonstrate with numerical experiments that: (i) the congestion game formulation allows us to efficiently compute equilibrium flows for each candidate charger placement; (ii) the greedy approach can closely approximate the optimal selection.